In this write-up, I will walk you through the steps I took to solve challenges in Defcon 32 Hackman CTF 2024. The CTF has 8 different challenges curated for network packet analysis.
Unraveling the Mysteries of Packet Analysis
Packet analysis is a fundamental skill in network security, allowing professionals to dissect network traffic, uncover hidden data, and expose potential security threats. This challenge put those skills to the test, requiring me to decode an encrypted message buried within network packets.
What is Defcon & Why Are These Challenges Important?
DEF CON isn't just a conference; it's a hacker's paradise—a gathering of the sharpest minds in cybersecurity, held annually in Las Vegas, Nevada. Since its inception in 1993, DEF CON has grown into the ultimate battleground for security researchers, ethical hackers, and digital outlaws who push the limits of technology. Attendees range from security pros and students to federal agents, all converging in an electrifying atmosphere of talks, workshops, and mind-bending challenges. Among its legendary contests, Capture the Flag (CTF) stands as the ultimate test of hacking prowess, where teams battle in high-stakes digital warfare to breach and defend systems. With lockpicking, social engineering, and even beer-cooling competitions, DEF CON is more than just a conference—it’s an experience that defines hacker culture.
The challenges simulate real-world scenarios, sharpening investigative and analytical skills essential for professionals in the field.
Why This Write-Up Matters
This guide aims to document the approach to solving packet analysis challenges. By leveraging the right tools and methodologies, I solved all the challenges.
Challenge 1: Welcome To Packet Analysis
This challenge is really straight forward. Clicking on the description of the link the link takes me to this site. Clicking on the google map link one can find the first flag to start the track with.
Challenge 2: Baby shark doo doo..
Challenge 2 Breakdown & Step-by-Step Solution
Step 1: Dissecting the Packet Capture
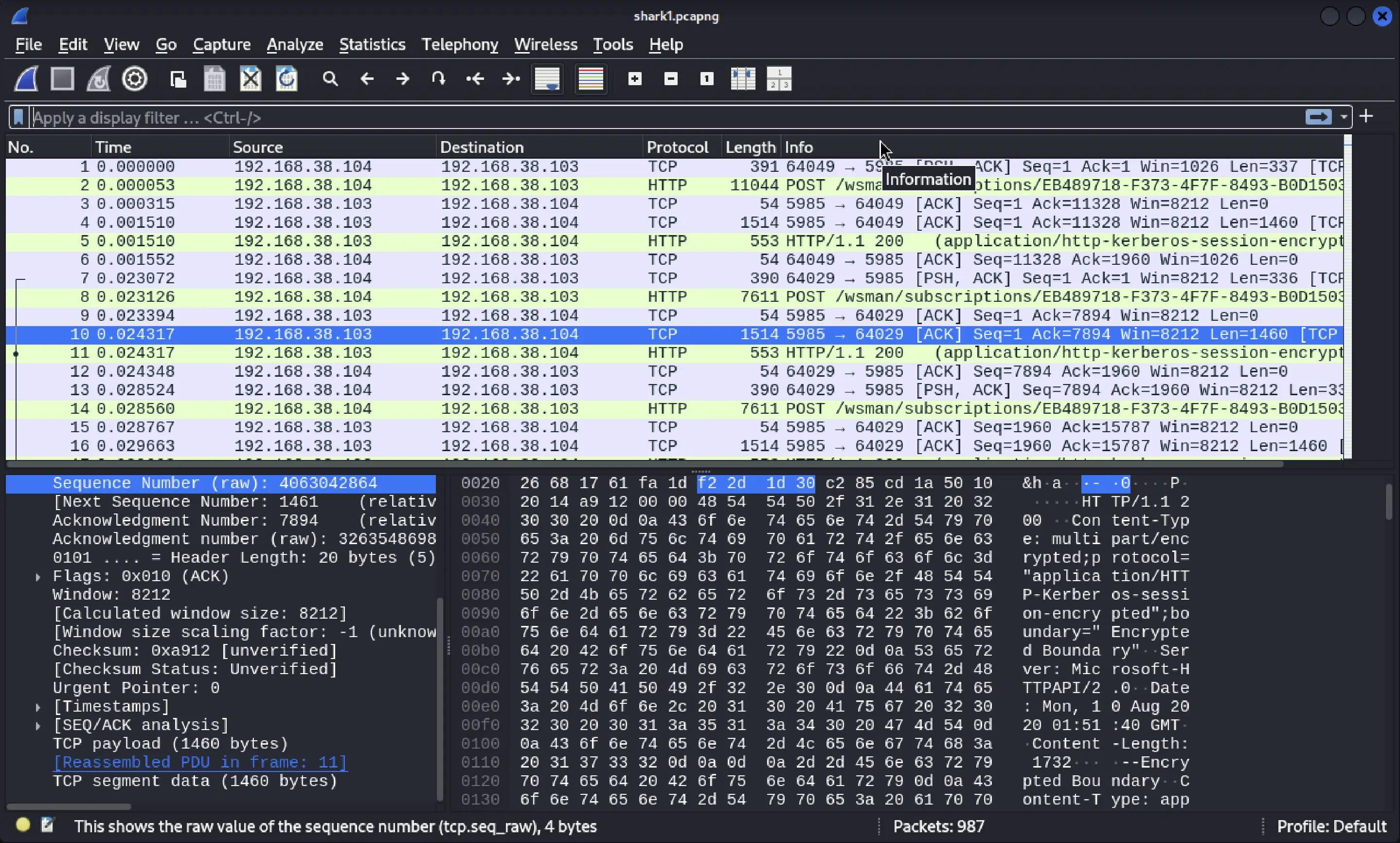
The challenge provided a file, shark1.pcapng, containing captured network traffic. I opened it in Wireshark, a powerful tool for analyzing network communications.
Key Findings:
Applying the filter tcp.stream eq 5 isolated the relevant TCP conversation.
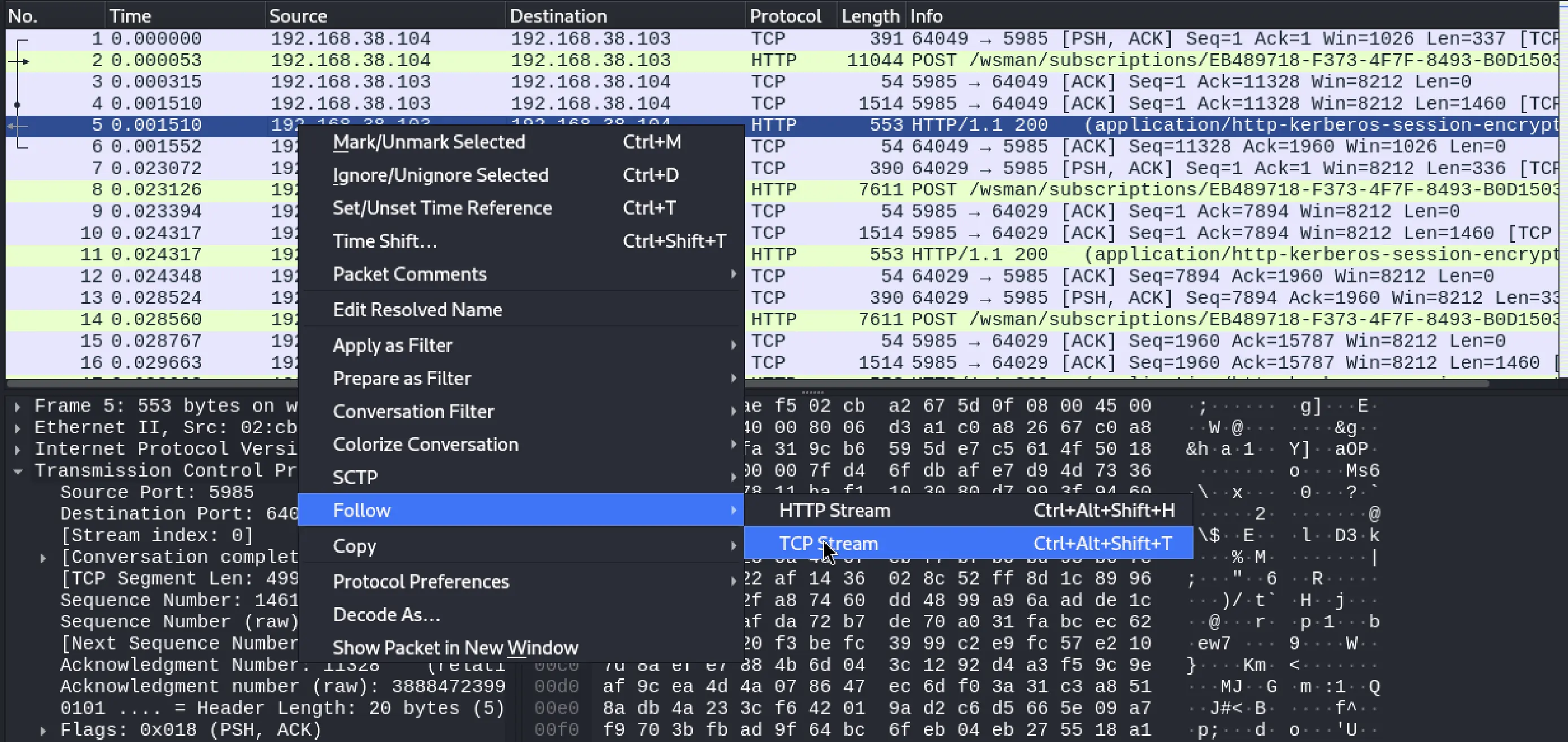
This conversation contained HTTP traffic, which, upon deeper inspection, revealed a suspiciously encoded text string.
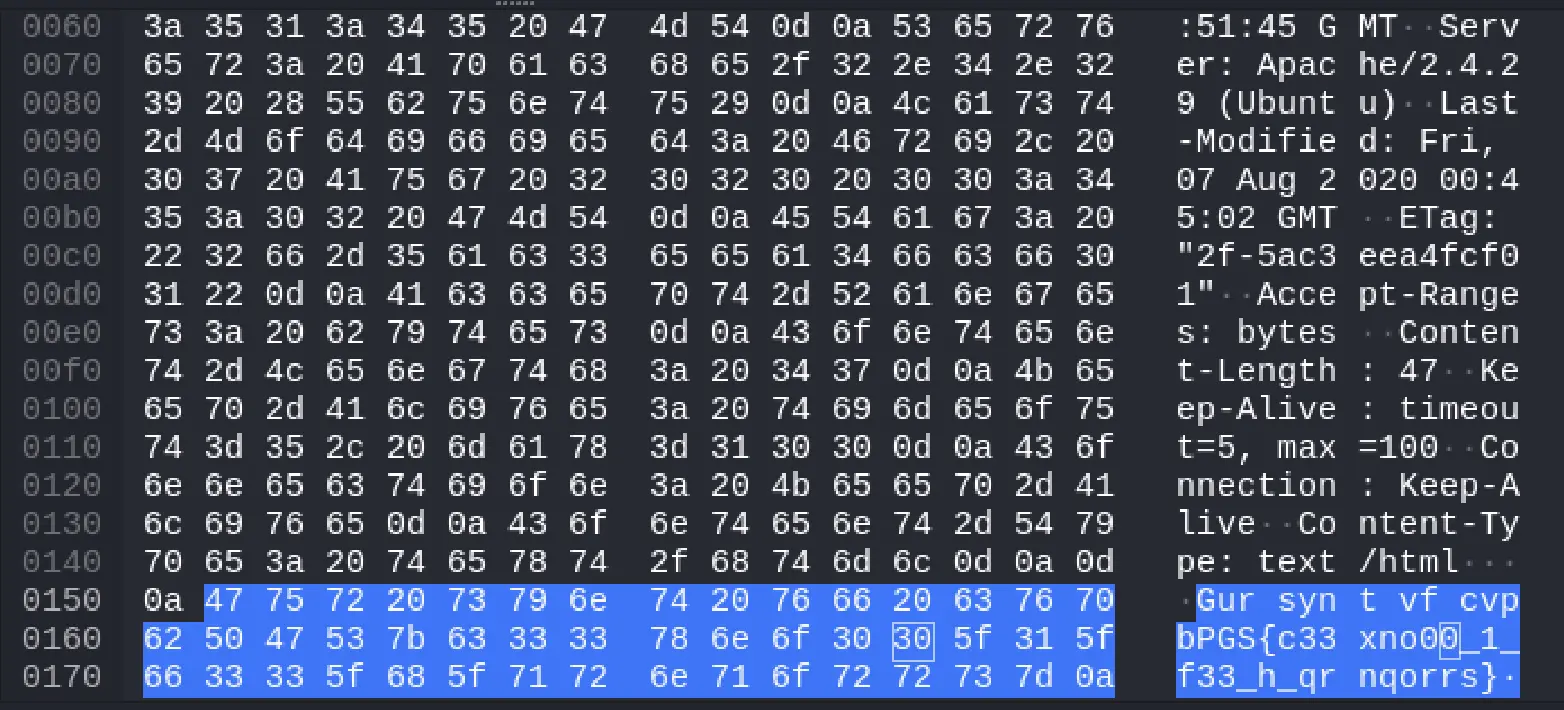
Extracted encoded message:
Gur synt vf cvpbPGS{c33xno00_1_f33_h_qrnqorrs}
This string was an immediate hint that it had undergone some form of obfuscation.
Step 2: Cracking the Cipher
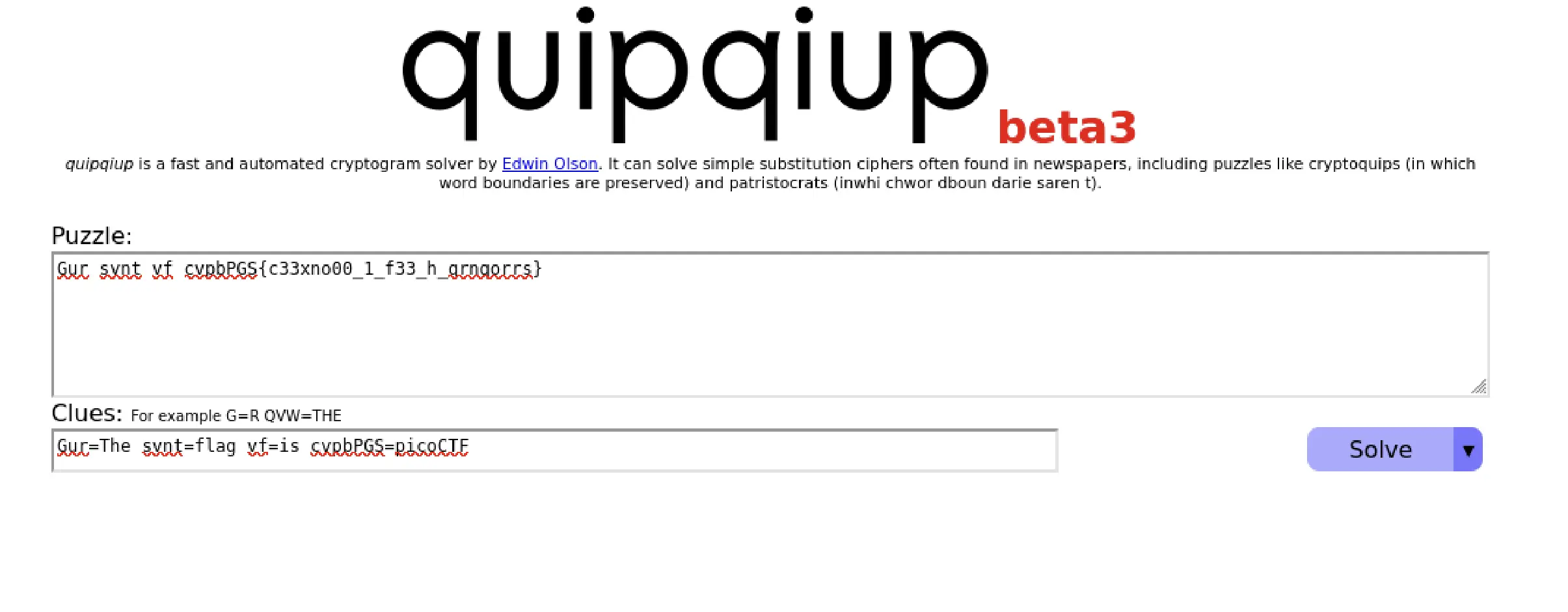
To determine the encryption method, I used quipqiup, an online cryptogram solver. It identified the message as being encoded with ROT13, a simple substitution cipher where each letter is shifted forward by 13 places in the alphabet.

Why ROT13?
ROT13 is a basic but effective encoding technique often used to obscure text in CTF challenges. Since it's a symmetric cipher, applying ROT13 again reverses the transformation, revealing the original message.
Step 3: Decrypting with CyberChef
With the encryption method identified, I used CyberChef, a powerful web-based tool for data manipulation, to decode the message.
Steps in CyberChef:
Pasted the encoded message into the input field.
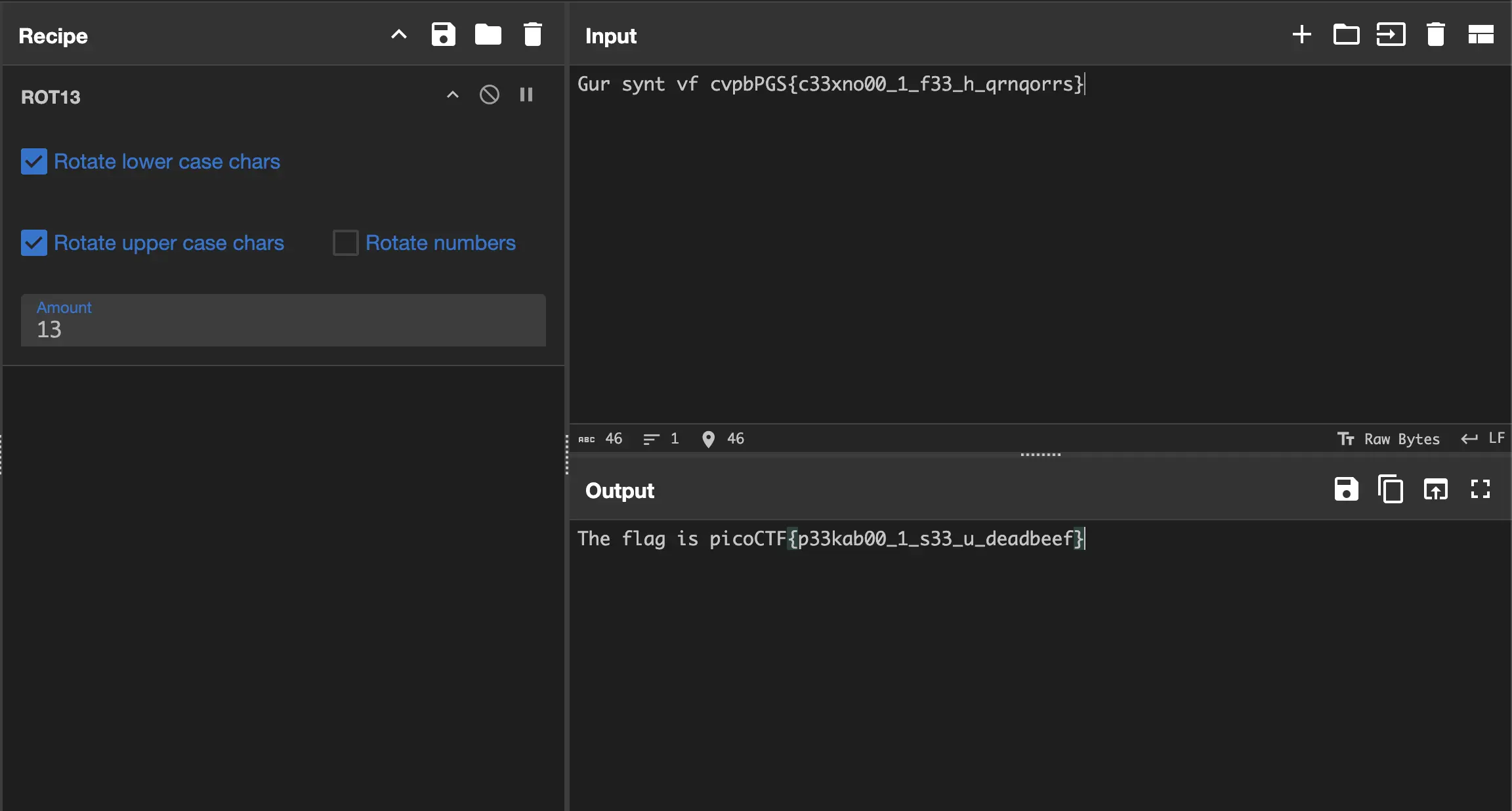
Applied the ROT13 decryption operation.
The original flag was revealed:
picoCTF{p33kab00_1_s33_u_deadbeef}
Success! The challenge was solved, and the flag was retrieved!
Challenge 3: Going Phishing!
Challenge 3 Breakdown & Solution
Step 1: Filtering HTTP Requests
Using Wireshark, I loaded the provided .pcapng file.
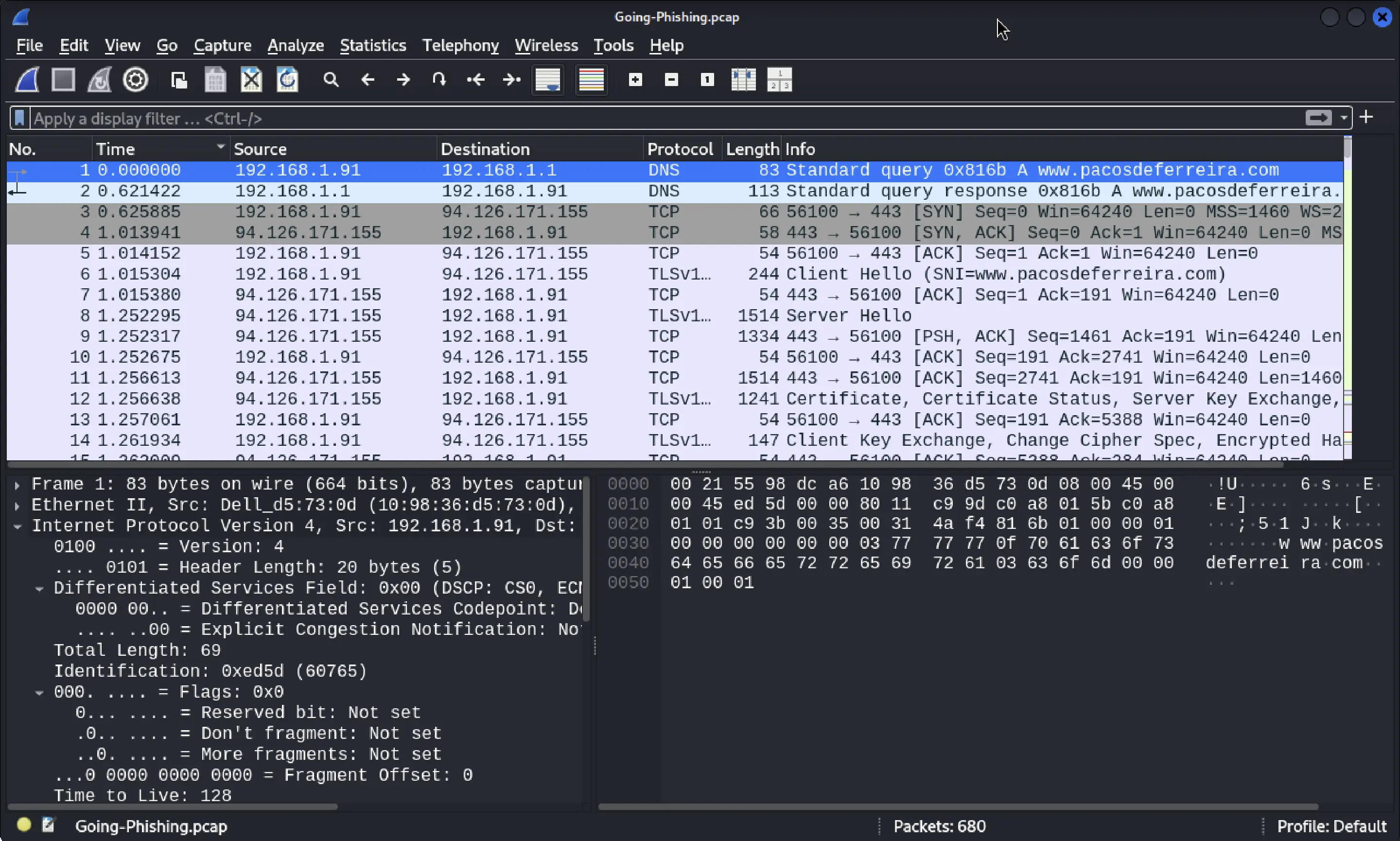
Since this challenge involves phishing, I applied the filter http.request. This shows GET/POST requests that might contain phishing attempts.
http.request
This revealed a suspicious single HTTP request stream.
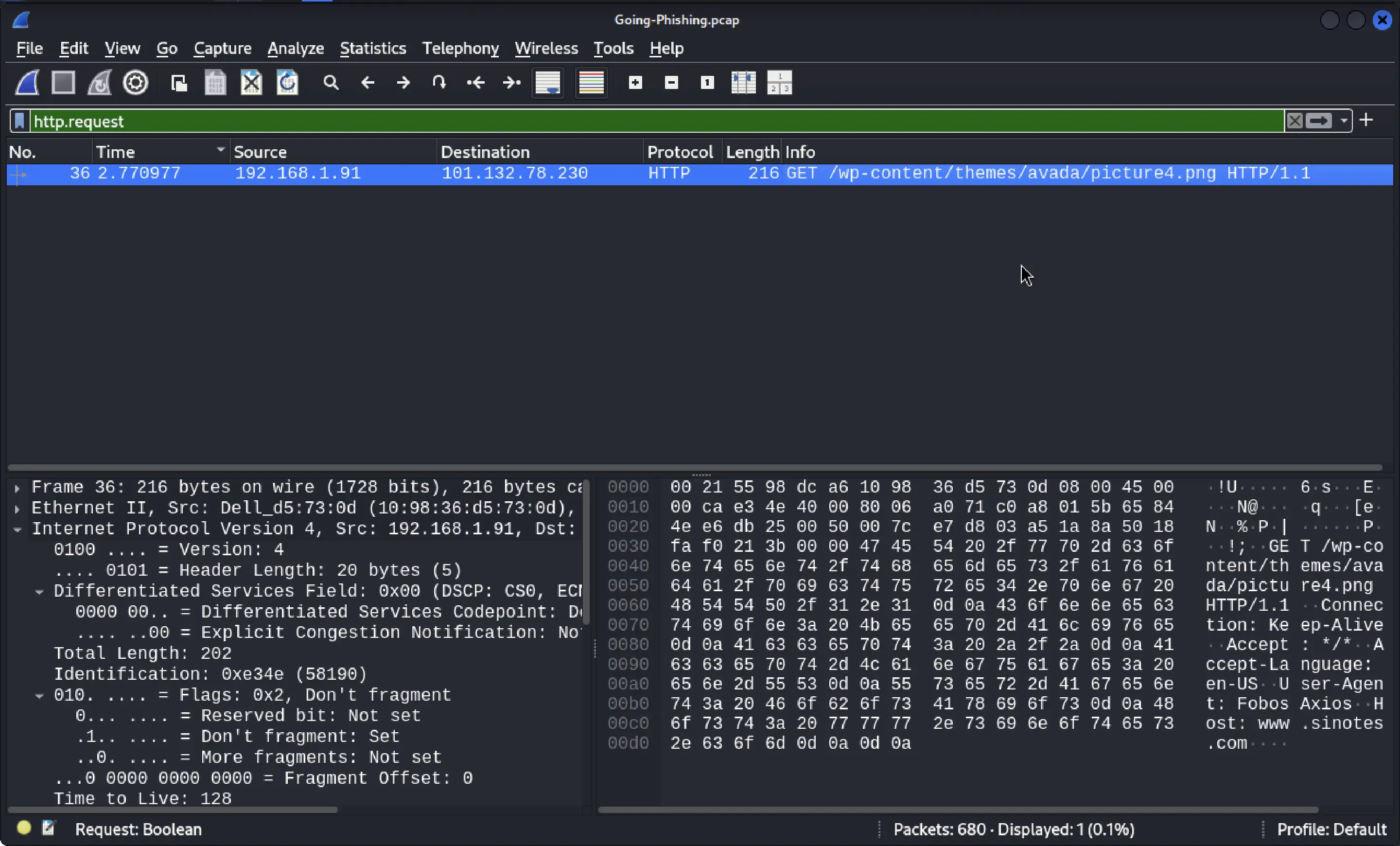
GET /wp-content/themes/avada/picture4.png HTTP/1.1
Connection: Keep-Alive
Accept: */*
Accept-Language: en-US
User-Agent: FobosAxios
Host: www.sinotes.com
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Fri, 24 Jul 2020 22:33:14 GMT
Server: Apache
Last-Modified: Sat, 11 Aug 2018 00:54:45 GMT
ETag: "31000-5731e4e64df40"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 200704
Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100
Connection: Keep-Alive
Content-Type: image/png
MZ.................@...............!..L.!This program cannot be run in DOS mode.
Step 2: Identifying Anomalous Data
The response indicated that picture4.png was actually an executable file, not a valid PNG image. The presence of the MZ header confirmed it was a Windows executable (.exe), likely hiding a payload.
Step 3: Investigating VirusTotal for the Host
A quick lookup of http://www.sinotes.com on VirusTotal flagged it as vulnerable, suggesting the server was either compromised or intentionally hosting malicious content.
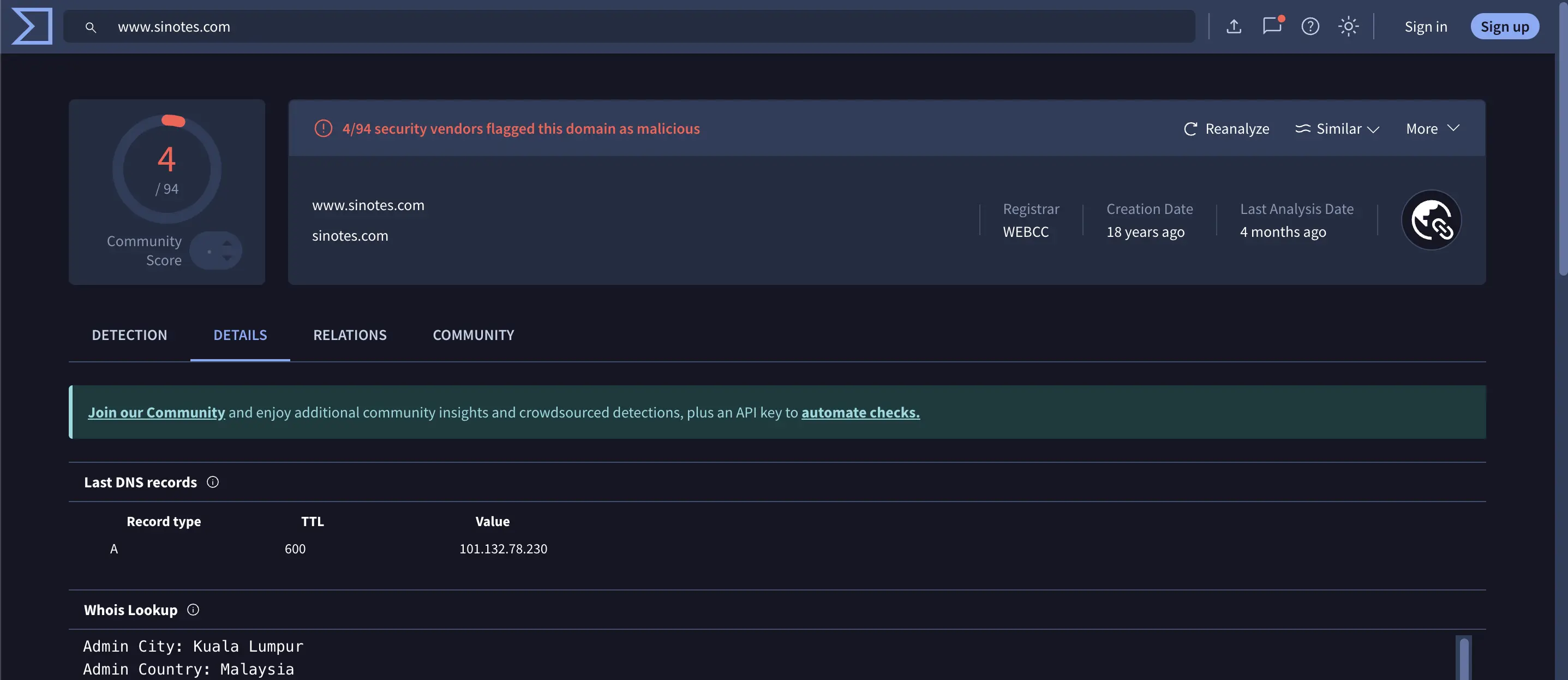
This suggests the server might have been compromised, potentially hosting malicious payloads or hidden data.
Step 4: Extracting and Analyzing picture4.png
I exported the file from Wireshark by navigating to File > Export Objects > HTTP and selecting picture4.png. Given the nature of the file, I renamed it to picture4.png.exe for further analysis.
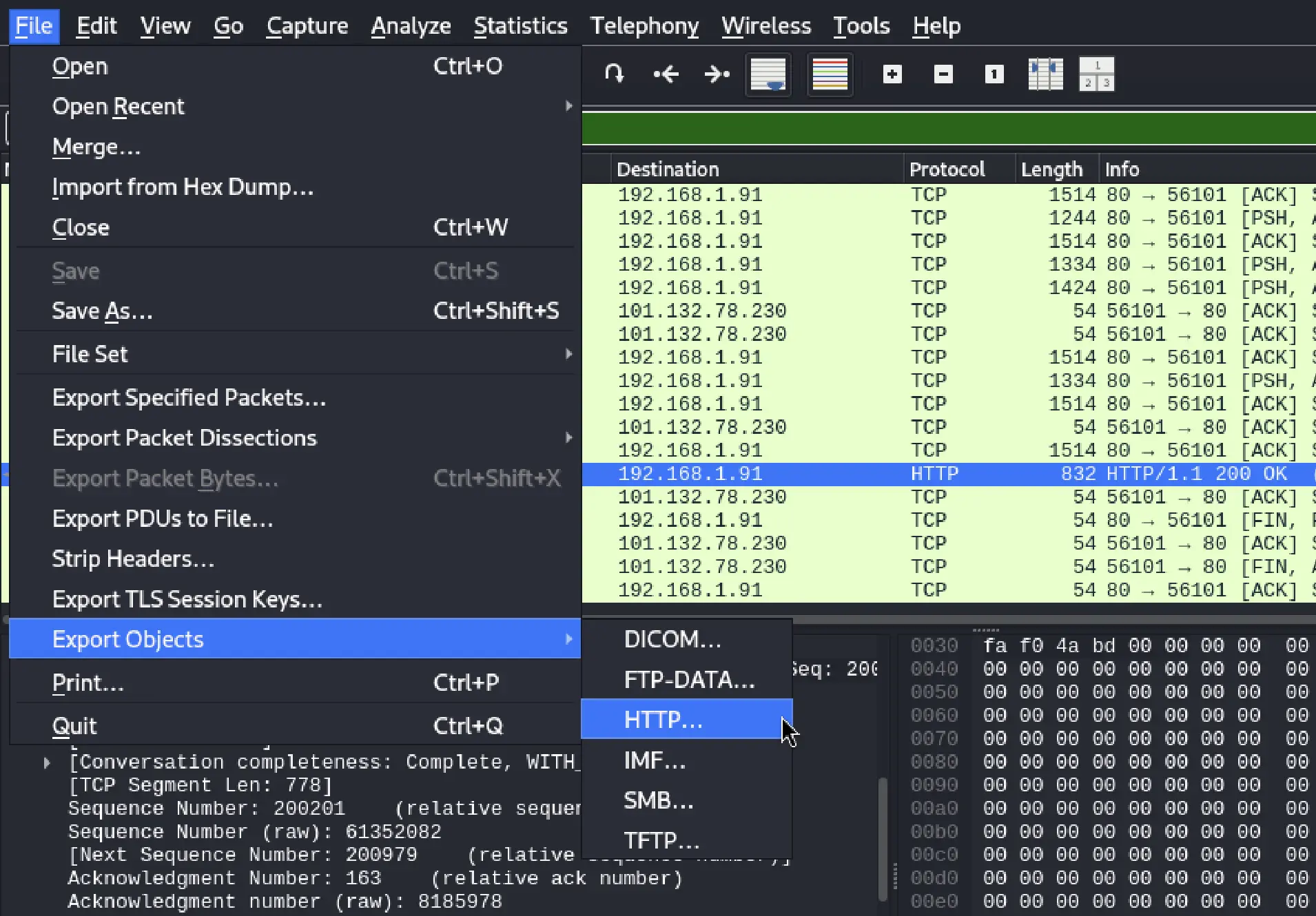
Renamed it to picture4.png.exe to reflect its actual format.
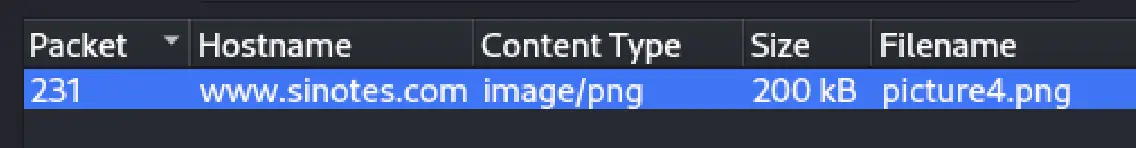
The executable might contain an embedded flag in its metadata or as part of the payload.
Step 5: Digging Deeper with VirusTotal
Upon closer inspection of the executable’s metadata, I discovered that its original filename was "oflor32", a Win32 executable.
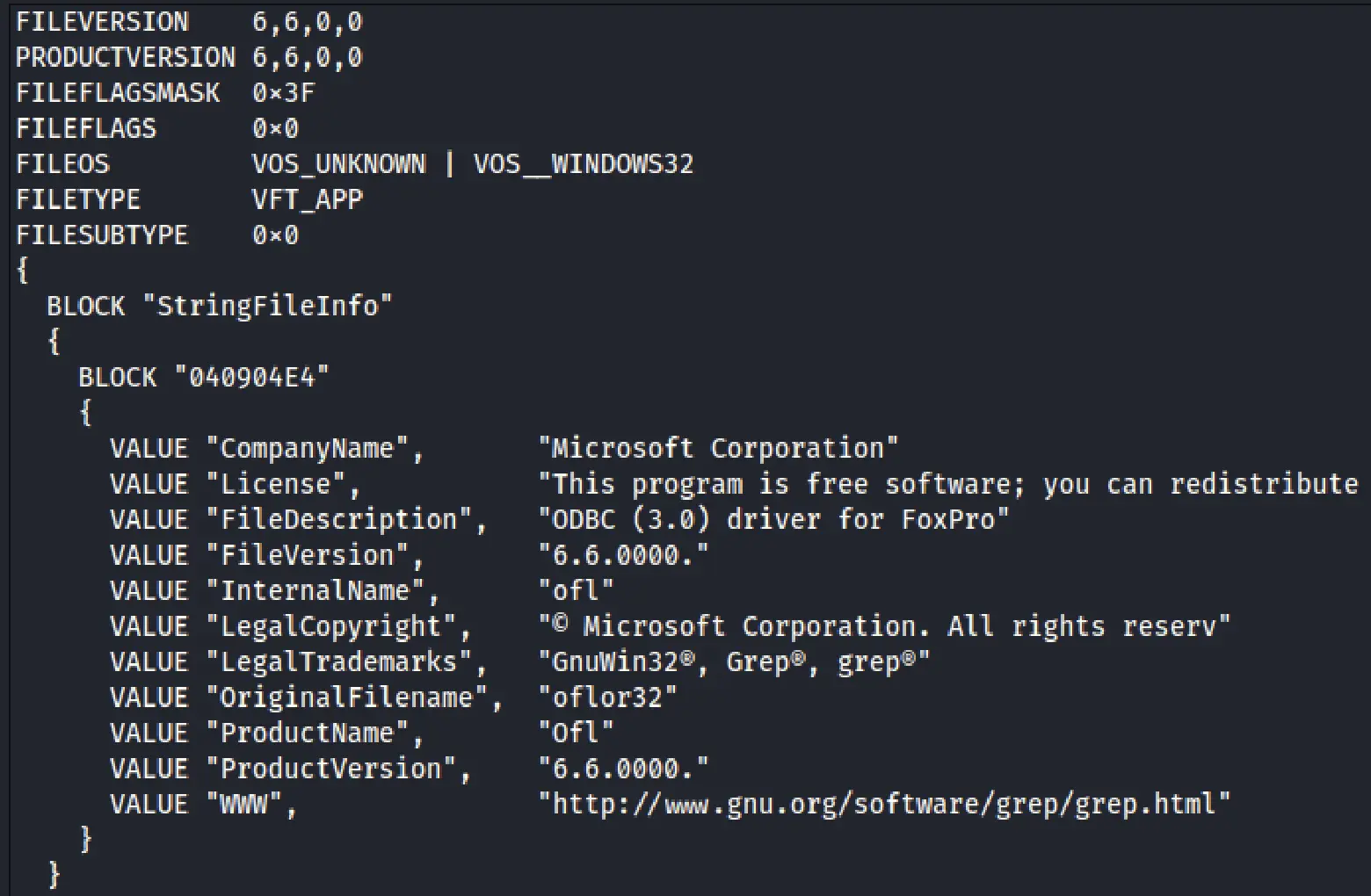
To proceed, I extracted its MD5 hash:
md5sum picture4.png.exe

Submitting the hash to VirusTotal confirmed multiple detections of the file as a threat.
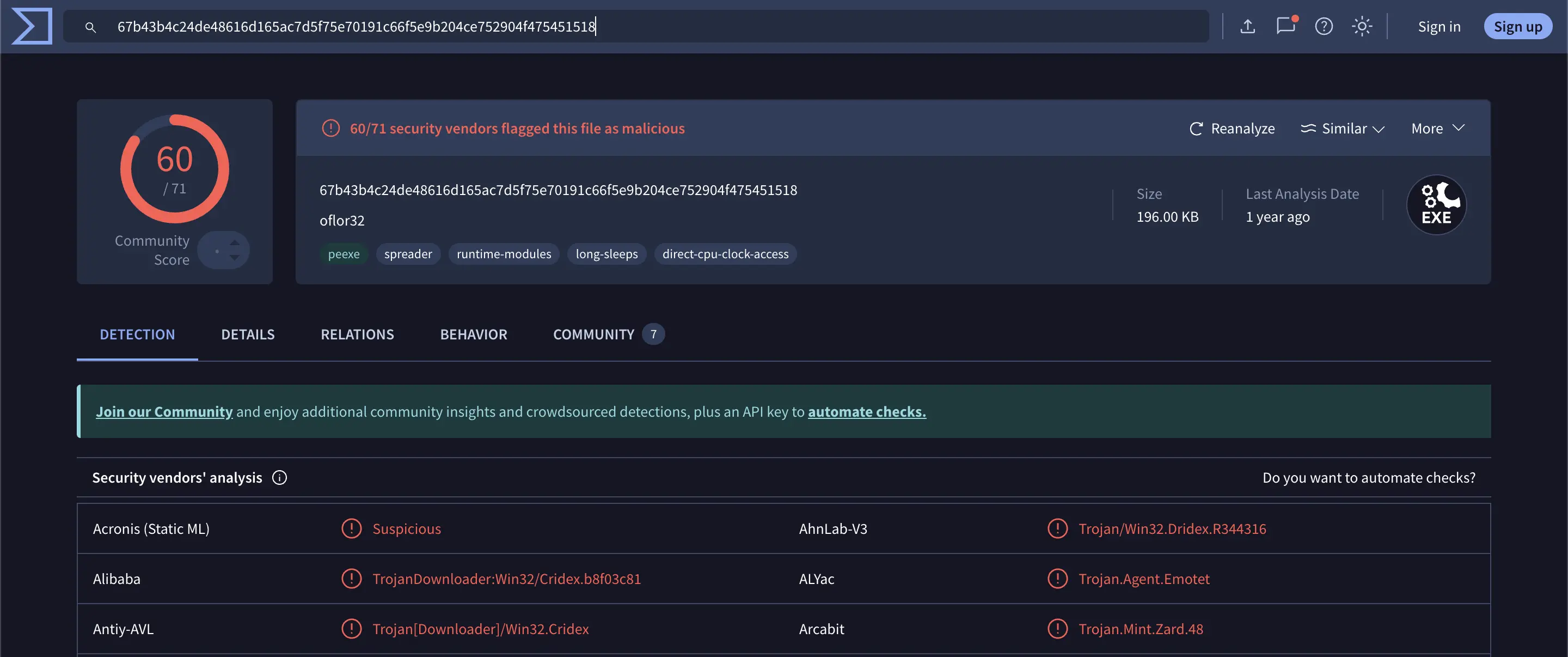
Digging into the Community section on VirusTotal, I found an intriguing URL shared by other analyst.
Step 6: Extracting the Flag
Following the link led me to an image containing the final flag.
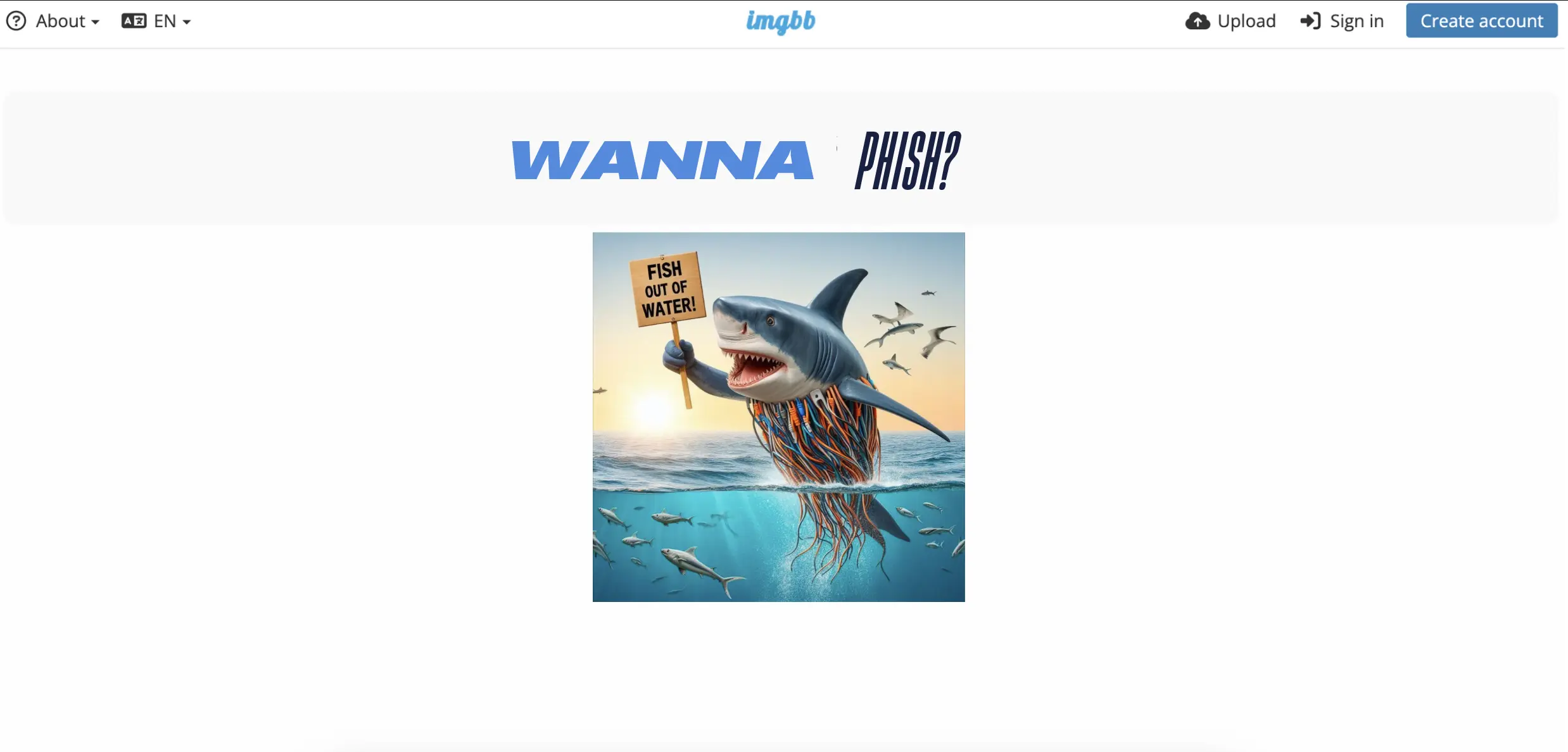
The original flag:
FISH IS OUT WATER



